One of the unfortunate truths in life is that every agricultural process exists at the mercy of Mother Nature. And because of this, even the slightest of changes in the global or regional climate patterns can fundamentally affect our farms, gardens, orchards, and vineyards that rely on very specific climate conditions.
Climate change and its implications for the future aren’t a secret, particularly for those who work in the wine industry. Wineries across the globe have had to face a variety of devastating situations over the last few years — uncontrollable wildfires, extreme polar vortexes, unexpected droughts, and inconsistent temperatures pogo-ing up and down despite the season.
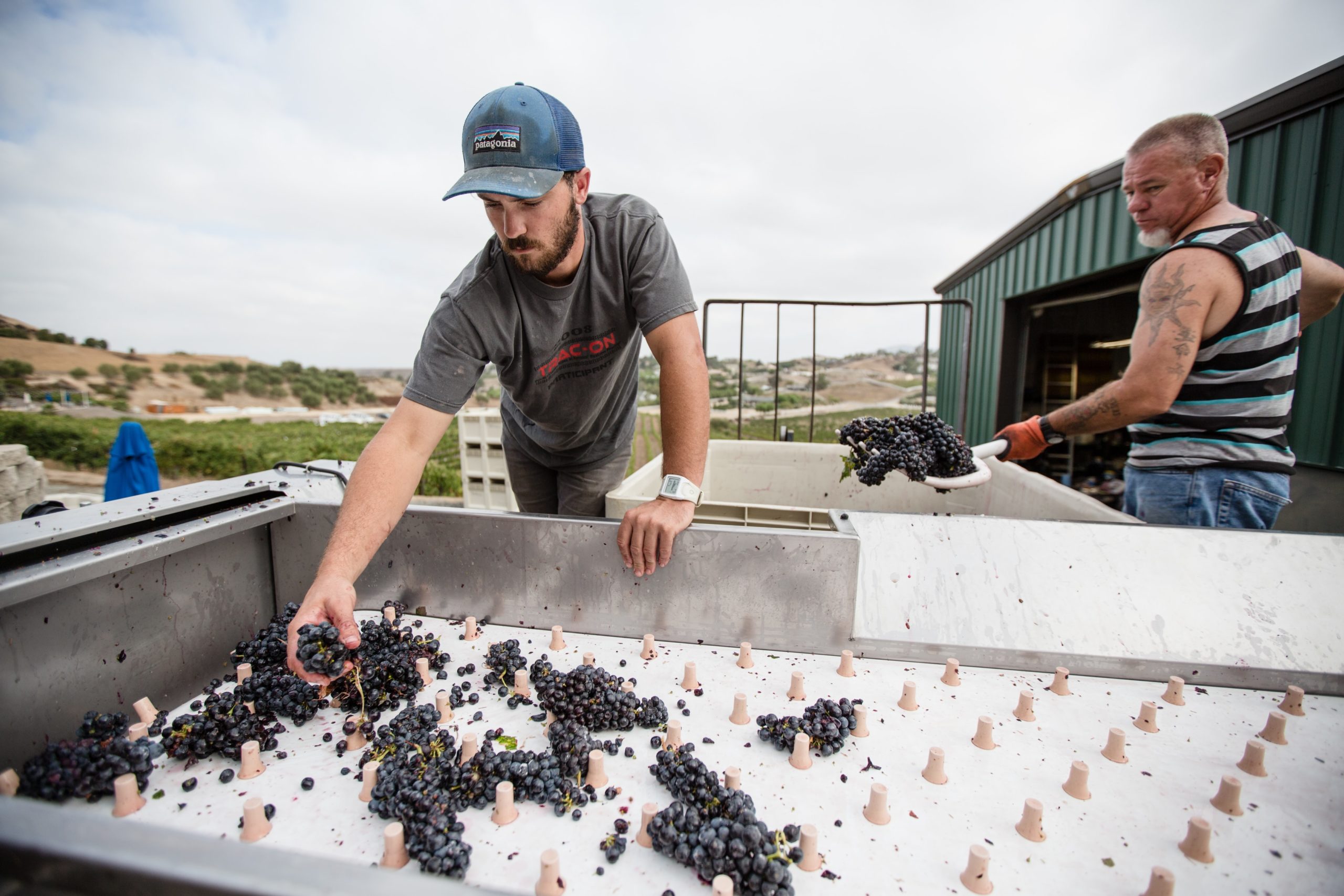
Wine production is already a notoriously fickle operation. Unlike other, more hardy fruit crops, wine grapes are extremely sensitive to their external environment, making it that much more of an exquisite and volatile product to produce. So what exactly are the implications of climate change in relation to grape farming and the larger wine industry as a whole?
Lack of Water
(Source: NOAA/NCEI via Weather.com)
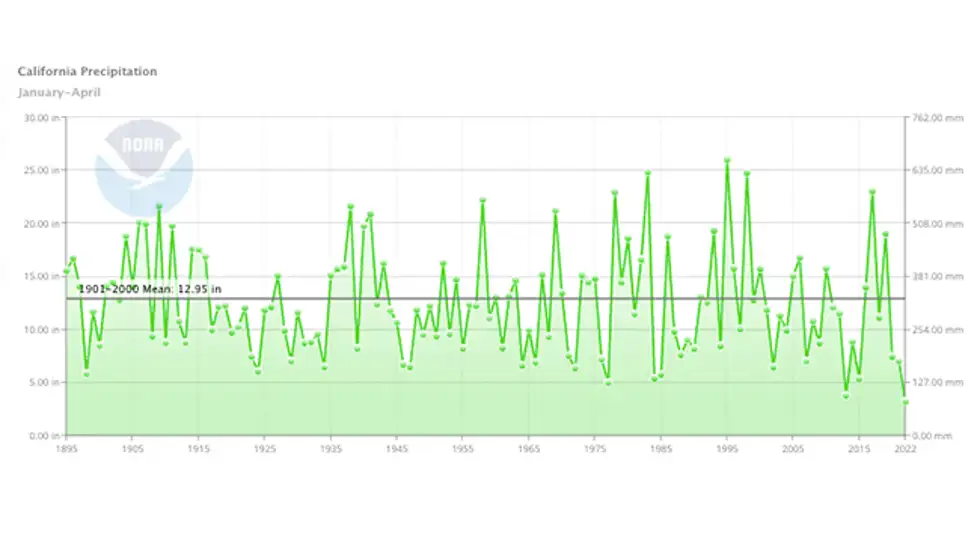
Like most agricultural processes, water will always play an essential part in grape production, which is why droughts often have long-lasting, devastating effects across the industry. The first four months of this year were the driest on record in the state of California, and much of the Southwest and Plains have also reported much drier conditions than usual. All of these factors have created the perfect storm with heightened potential for drought.
Historically, drought season has been known to affect both the quantity and the size of grapes, decreasing each crop’s overall potential yield. Even the most modest of droughts can put pressure on that delicate balance between animals, plants, and people who all rely on water to survive.
For wineries, a lack of water for any period of time means the volume of grapes harvested will be significantly less substantial. And over a prolonged period of time, these circumstances will lead to both grape and wine shortages down the road. But on a positive note, a lack of water can decrease the potential growth of molds and mildews in grape crops.
One of the most important things you can do to prepare for these potential drought seasons is to purchase additional acreage to expand the vineyard and increase the initial grape yield.
Danger of Wildfires
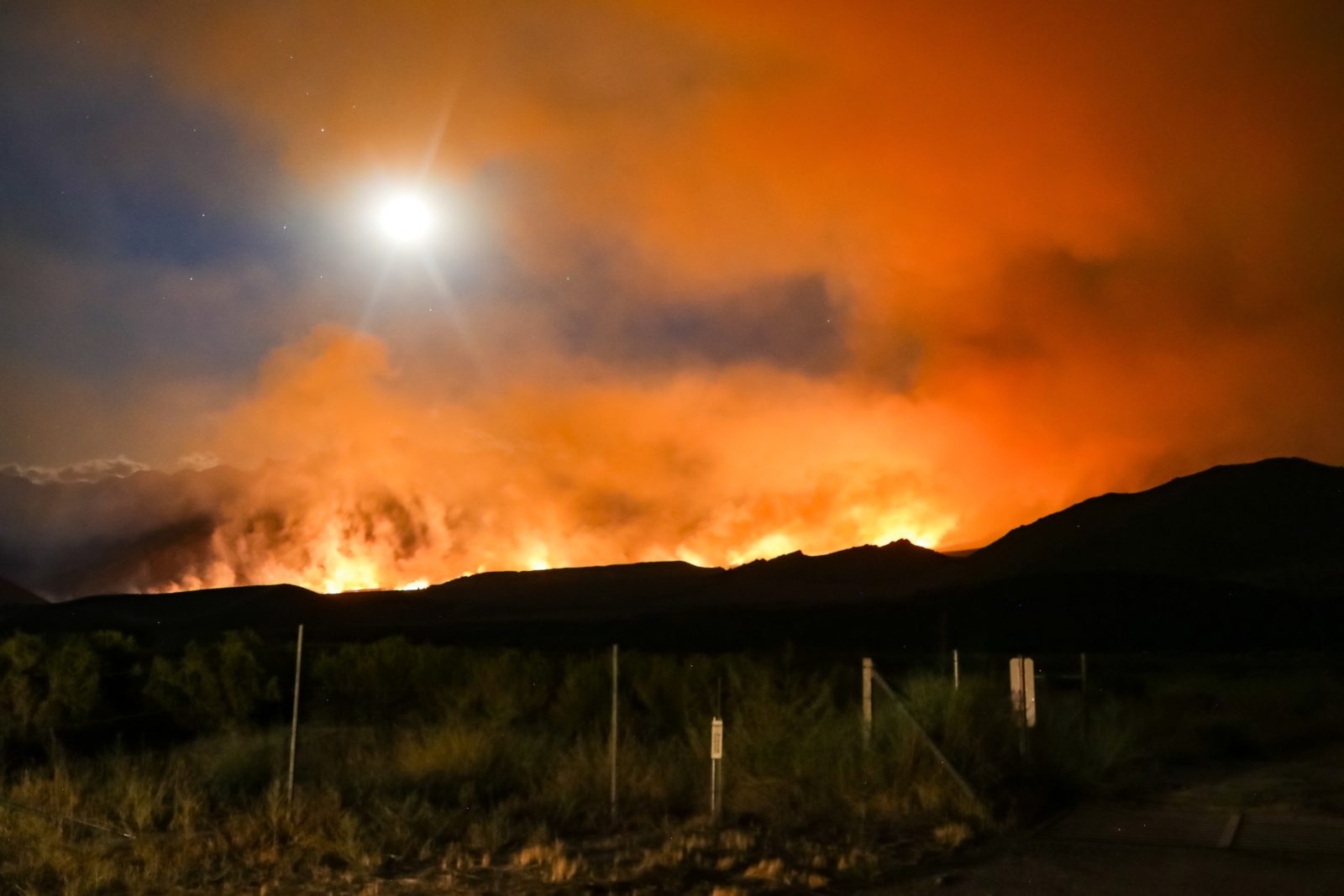

Another unfortunate element that the agricultural industry must face year after year are the raging wildfires that tear through farms and vineyards. Wine Country is no stranger to watching powerlessly as massive walls of fire make their way across the Golden State and beyond, scorching everything in its path.
Fortunately for most, grapevines put up a strong fight against wildfire, serving as fire breaks with limited fuel to burn. This can save wineries from experiencing further damage by stopping the flames from spreading further across the property.
But the physical flames aren’t the only elements to fear from wildfires — even more damage can result from the fire’s intense heat and the strong smoke that comes with these infernos. Even in instances where crops remain largely untouched by the scorching blaze, grapes exposed to high levels of smoke can produce wines with undesirable sensory characteristics like burnt, ashy, or medicinal flavor profiles. And the worst part is that these potentially tainted grapes won’t be detectable until after they’ve completed the fermentation process and are in their final form.
Managing Wildfire Risk for Your Winery
In order to protect your winery during the annual wildfire season, there are a few precautionary measures you can take. First, it’s crucial to understand the extent that prospective wildfires pose to your vineyard’s location and find ways to mitigate the largest hazards proactively.
Fire prevention and mitigation are important measures to take by creating a defensible space around your vineyards and winery. This can include removing any potential flammable trees, brush, and combustible items from the property to stop the spread of fire before it starts.
It’s also important to have a plan in place for your team to follow in case of emergency. When fire strikes, every second counts — make sure your team understands how to respond as quickly and seamlessly as possible by creating a well-known written emergency and evacuation plan.
Lastly, be sure to regularly review your insurance policy limits and make sure you have the right amount of coverage to protect your business against potential fire losses.
Insurance Pricing Increases
Unfortunately, you may have already noted this major effect of climate conditions in recent years. As with most industries, wineries have reported that insurance prices continue to rise. In fact, Silicon Valley Bank’s recent State of the Industry report noted that 70% of respondents said their insurance costs increased in 2021 and are likely to continue to rise in following years.
As these prices increase, many wineries are struggling to find sufficient coverage for their businesses, putting them in the precarious situation of losing everything in dire circumstances. This issue also prevents winery owners from getting the financial assistance and loans that they need to stay afloat during economic hardships.
Despite the rising costs, the right insurance coverage is a necessary tool to protect against heightened farming and climate-related risks.
Differing Harvest Seasons & the Emergence of New Wine Regions

Gone are the days of a regulated four-season calendar year. Harvest time for all crops can be expected to begin earlier and earlier each year, and for grape growers in certain regions of the world, this means losing precious weeks over time.
Grapes are known for their delicate skins that can burst easily if their harvest period is delayed for any significant amount of time. So, thanks to rising temperatures, the ripening process for grapes is sped up. This means farmers have to throw their carefully laid plans to the wind and instead opt to keep a careful eye on the yield throughout the entire season.
Now, grapes are ready to start growing much earlier in the season as winters become milder year over year. And these changes also mean that familiar wine regions are shifting from their once-normal geographies to new locations. After all, California wineries can’t continue to produce the same varietals as temperatures rise and plummet sporadically each season. And by the same token, areas that were previously too cold to produce successful grape crops like Michigan and Southern Ontario are now displaying more hospitable climates and have unbridled access to fresh water from the Great Lakes.
Today, climate change continues to disrupt nearly every facet of our lives, including both our work and play. But together, with proper planning and preparation, we as consumers and businesses alike can help our beloved wineries adapt to these changes in stride.



